In the world of construction and plumbing, even the smallest component can be the difference between a dry, secure structure and one plagued by water damage. A puddle flange is one such critical, yet often overlooked, component. It is a specialized device designed to create a watertight seal where a pipe penetrates a concrete structure, such as a wall, floor, or basement. Without this essential seal, water can easily travel along the outside of the pipe, leading to leaks, structural deterioration, and potential health hazards from mold or radon gas.
This guide provides a comprehensive look at puddle flanges, explaining how they work, the different types available, their key applications, and the industry standards that govern their manufacture. Understanding these elements is crucial for engineers, architects, contractors, and anyone involved in building durable and water-resistant structures.
Table of Contents
What is a Puddle Flange and How Does It Work?
A puddle flange, sometimes called a leak control flange or seep ring, is a circular, disk-like device that is installed around a pipe before it is embedded into concrete. Its primary purpose is not to connect pipes, but to act as a barrier within the concrete itself, preventing water from seeping through the gap between the pipe and the surrounding structure.
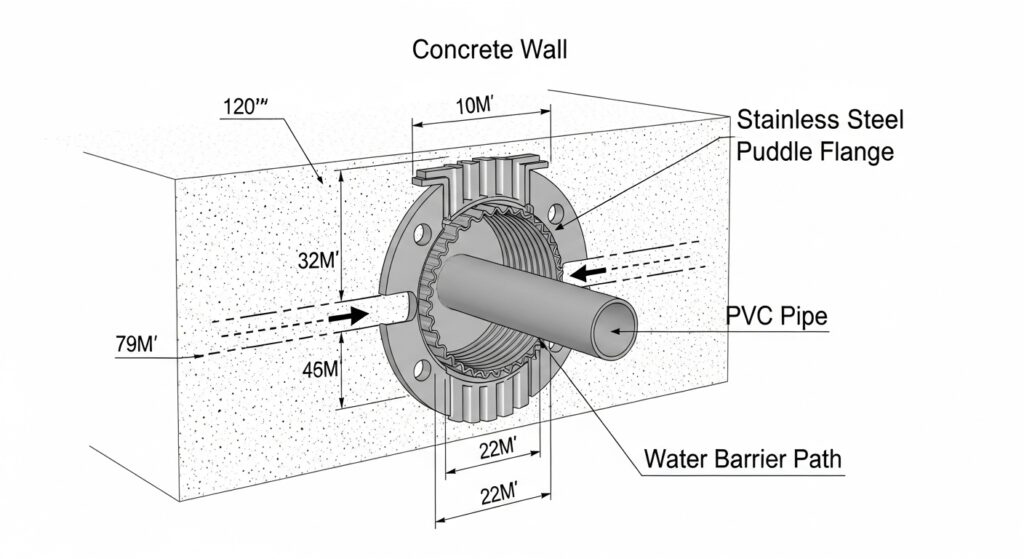
The principle behind a puddle flange is simple but effective. Water naturally seeks the path of least resistance and can easily migrate through the tiny interface between a pipe and concrete. The puddle flange interrupts this path. When concrete is poured, it bonds with the large surface area of the flange, creating a physical obstruction. As the concrete cures and shrinks, this integrated barrier prevents water from tracking along the pipe’s exterior, effectively “short-circuiting” the potential leak path.
Common Types of Puddle Flanges and Their Materials
Puddle flanges are available in various types and materials to suit different applications, environmental conditions, and pipe materials. The choice of material is critical for ensuring durability and long-term performance.
Table: Comparison of Common Puddle Flange Materials
Specialized Flange Designs
Beyond material differences, specialized designs cater to specific needs:
- Dual Puddle Flanges: These modern designs, often made from EPDM rubber and stainless steel bands, offer enhanced protection against both water leakage and radon gas infiltration. They are designed for faster installation and provide a robust seal as the concrete cures and shrinks.
- Flanges for Flooring Systems: Specific puddle flange variants are designed for different floor types. Tiled floor flanges typically feature a large PVC base for membrane bonding, while vinyl floor flanges use a clamping ring to secure the waterproof vinyl membrane directly.
Key Applications and Industries
Puddle flanges are indispensable in any construction scenario where pipes pass through concrete structures below or at ground level. Their most common applications include :
- Basements and Underground Structures: Preventing groundwater ingress through pipe penetrations in walls and floors.
- Water and Sewage Treatment Plants: Sealing pipes in tanks, pump stations, and manholes.
- Swimming Pools and Water Tanks: Ensuring a watertight seal for inlet and outlet pipes.
- Tunnels and Subways: Protecting infrastructure from water seepage.
- Shafts and Service Ducts: Maintaining the integrity of waterproof concrete barriers.
Puddle Flange Standards and Specifications
To ensure reliability and performance, puddle flanges are manufactured according to various international standards. These standards govern materials, dimensions, and pressure ratings, ensuring compatibility and safety.
Table: Key Industry Standards for Puddle Flanges
These standards provide a framework for quality, ensuring that puddle flanges can perform their critical sealing function under designated pressure and environmental conditions .
Installation Tips and Common Challenges
Proper installation is paramount to the performance of a puddle flange. Here are some key considerations:
- Pre-Fitting: Always pre-fit the flange onto the pipe before embedding it in concrete. Ensure it is centered within the formwork.
- Concrete Coverage: The concrete must fully surround the flange with no voids. A common guideline is to ensure a minimum of 2 inches (50 mm) of concrete cover on all sides.
- Surface Preparation: For optimal bonding, the surface of the flange that will be in contact with concrete should be clean and free of oils or debris.
- Pipe Support: Puddle flanges do not provide axial restraint. The pipe must be independently supported to withstand the forces of the concrete pour without moving.
- Addressing Shrinkage: Some installers use water-swelling tape in conjunction with the flange to create an even more robust seal that compensates for concrete shrinkage over time.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary purpose of a puddle flange?
The primary purpose of a puddle flange is to create a watertight seal where a pipe passes through a concrete structure, preventing water from tracking along the external surface of the pipe and causing leaks.
2. Can a puddle flange be installed after the concrete is poured?
No, puddle flanges are designed to be cast directly into the concrete when it is poured. This allows the concrete to bond with the flange, creating an integral barrier. Retrofitting a puddle flange after construction is very difficult and ineffective.
3. How do I choose the right puddle flange material?
The choice depends on the application environment. Use stainless steel for corrosive or harsh environments, PVC for standard residential plumbing, and rubber (EPDM) where slight pipe movement is expected or for superior sealing against gases like radon.
4. Do puddle flanges protect against radon gas?
Yes, specific designs like dual puddle flanges are engineered to provide a barrier against not only water but also radon gas and other hydrocarbons, preventing them from seeping into the building through pipe penetrations.
5. What is the difference between a puddle flange and a standard pipe flange?
A standard pipe flange (e.g., weld neck, slip-on) is used to connect two sections of pipe together. A puddle flange is not a connecting point; it is a sealing device that gets embedded in concrete to prevent water migration around a single pipe.
6. What are the consequences of a failed puddle flange?
A failed puddle flange can lead to persistent water leakage, which can cause mold growth, damage to building finishes, corrosion of structural reinforcements, and in severe cases, compromise the structural integrity of the concrete.
7. Where can I find size charts for puddle flanges?
Manufacturers and suppliers provide detailed dimension charts. These typically list Nominal Diameter (DN), Outside Diameter, Inside Diameter, Thickness, and Bolt Hole details. You can find these charts on specialized piping websites.
Conclusion
A puddle flange may be a simple component, but its role in modern construction is vital. By effectively preventing water ingress at pipe penetrations, it protects investments and ensures the long-term durability and safety of structures from basements to major infrastructure projects. Selecting the correct type and material for your specific application, ensuring it meets relevant industry standards, and following proper installation procedures are the keys to achieving a leak-free, reliable result. Understanding what a puddle flange is and how it works is fundamental knowledge for anyone committed to quality construction.
For all your Puddle Flange requirements, consult with reputable manufacturers and suppliers like Texas Flange, who can provide the right flange solutions tailored to your application’s demands.